Digital Risk Twin
The MADE platform creates and maintains a Digital Risk Twin. MADE is the first software platform to introduce a model-based approach to RAMS, offering a proven solution to traditional RAMS challenges by providing a virtual representation of a system design, physical system functionality and processes. Here’s an in-depth look at what makes the MADE Digital Risk Twin a game-changer in the RAMS space for you and your organization.
What is a Digital Risk Twin?
The Digital Risk Twin (DRT) uses a simulation model of a system to identify & analyse potential failures / hazards & their consequences. Each risk can be objectively identified and analysed based on:
- system configuration (functional requirements & dependencies)
- safety impact
- operational impact
- context (environmental, mission profile, operating tempo, logistics approach, etc.), and
- cost of ownership impact
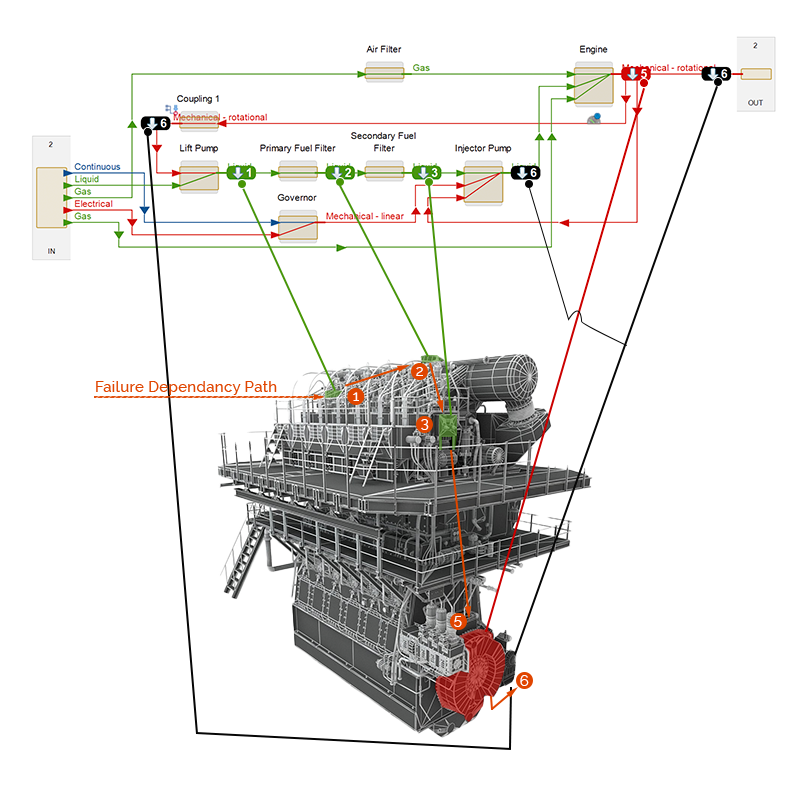
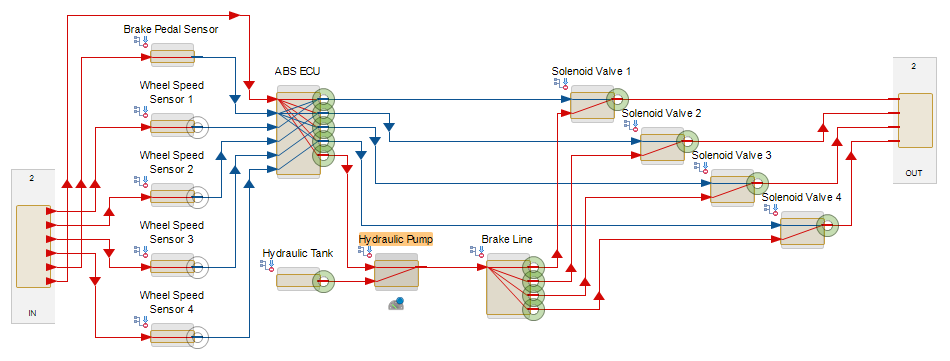
This image shows the failure propagation identified by MADE's digital risk twin through the injection of a failure in the coupling assembly.
Digital Risk Twin Definition
"A Digital Risk Twin is a Digital Twin, or a digital representation of an intended, or actual physical product that contains the necessary information in terms of functions, flows, components and other criteria that allows a risk simulation to be undertaken, identifying the risks (failures) of a system during operation and their path of propagation through the system."
MADE & the Digital Risk Twin
MADE is an advanced modeling tool designed to generate a dynamic virtual replica of real-world systems with a focus on risk management. This advanced digital model accurately mirrors physical assets, processes, and operations, enabling organizations to monitor, analyze, and manage risks in a proactive and controlled manner. In addition to risk management, MADE enhances the assessment of system availability and maintainability, offering a comprehensive solution for optimizing performance and mitigating potential issues.

Core Features of a Digital Risk Twin
- Autonomous Risk Analysis-A DRT autonomously establishes dependencies and impacts of potential failures in a system. It auto-generates various analyses to help identify the best mitigation strategies, streamlining the RAMS (Reliability, Availability, Maintainability, and Safety) process.
- Integrated Data Management-A DRT integrates information from all stages of the product lifecycle, ensuring consistent and up-to-date data management. This integration helps in maintaining traceability between activities and decisions related to identified risks.
- Visualization and Simulation-Key features of a DRT include advanced visualization tools that depict risk propagation and failure impacts across the system. This helps engineers understand complex risk scenarios and make informed decisions.
- Automated Processes-By automating data exchange and analysis, a DRT reduces manual data entry and replication. This improves efficiency and accuracy in risk assessments and system optimizations.
Challenges Addressed by a Digital Risk Twin
- Handling Complexity-Modern engineering systems are increasingly complex, with numerous components across various domains. A DRT helps manage this complexity by providing a unified view of system risks and dependencies.
- Ensuring Data Currency-Multiple teams often work on different parts of a system, leading to challenges in maintaining current and consistent data. A DRT ensures that updates in one area automatically reflect across all related analyses.
- Reducing Manual Effort-Manual data entry and analysis can be time-consuming and error-prone. A DRT automates these processes, allowing engineers to focus on high-value tasks such as risk identification and mitigation.
Implementing a Digital Risk Twin
- Risk Knowledge Capture-A DRT captures and shares comprehensive risk models and their causes, which is crucial for RAMS standards and processes.
- Support for RAMS Analyses-The DRT supports various safety assessment processes, including Functional Hazard Assessments (FHA) and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), ensuring alignment with industry standards.
- Optimization and Data Reuse-Optimizing RAMS analyses and leveraging data across projects are key benefits of a DRT. This includes reusing data and knowledge from previous analyses to expedite future projects.
- Integration with Design and Operations-A DRT integrates with both design and physical systems, providing valuable feedback to enhance system safety and performance throughout the lifecycle.
Benefits of Using a Digital Risk Twin
- Enhanced Design Optimization-A DRT optimizes the design process by automating RAMS analyses and providing actionable insights that improve system reliability and safety.
- Improved Analysis Quality-With higher data fidelity and better visualization, a DRT enhances the quality of RAMS outputs, leading to more reliable and safe designs.
- Faster Future Developments-The reuse of data and models accelerates future design processes, enabling quicker adaptation and iteration.
- Comprehensive Documentation-A DRT provides detailed documentation of RAMS requirements, decisions, and changes, which is crucial for audits and certifications.
- Competitive Advantage-Utilizing a DRT can differentiate a company in the marketplace, offering enhanced capabilities and a robust framework for managing system risks.
Analyses produced from a Digital Risk Twin
The following illustrates some of the analyses that can be conducted using a model-based approach, specifically a Digital Risk Twin (DRT), within RAMS assessments. The adoption of a Digital Risk Twin facilitates simplified and efficient analysis iterations at the push of a button, eliminating the need to track modifications across multiple systems and disciplines. This approach significantly reduces the risk of human error, which is prevalent in complex, mission-critical systems and can lead to avoidable critical errors in RAMS analyses.
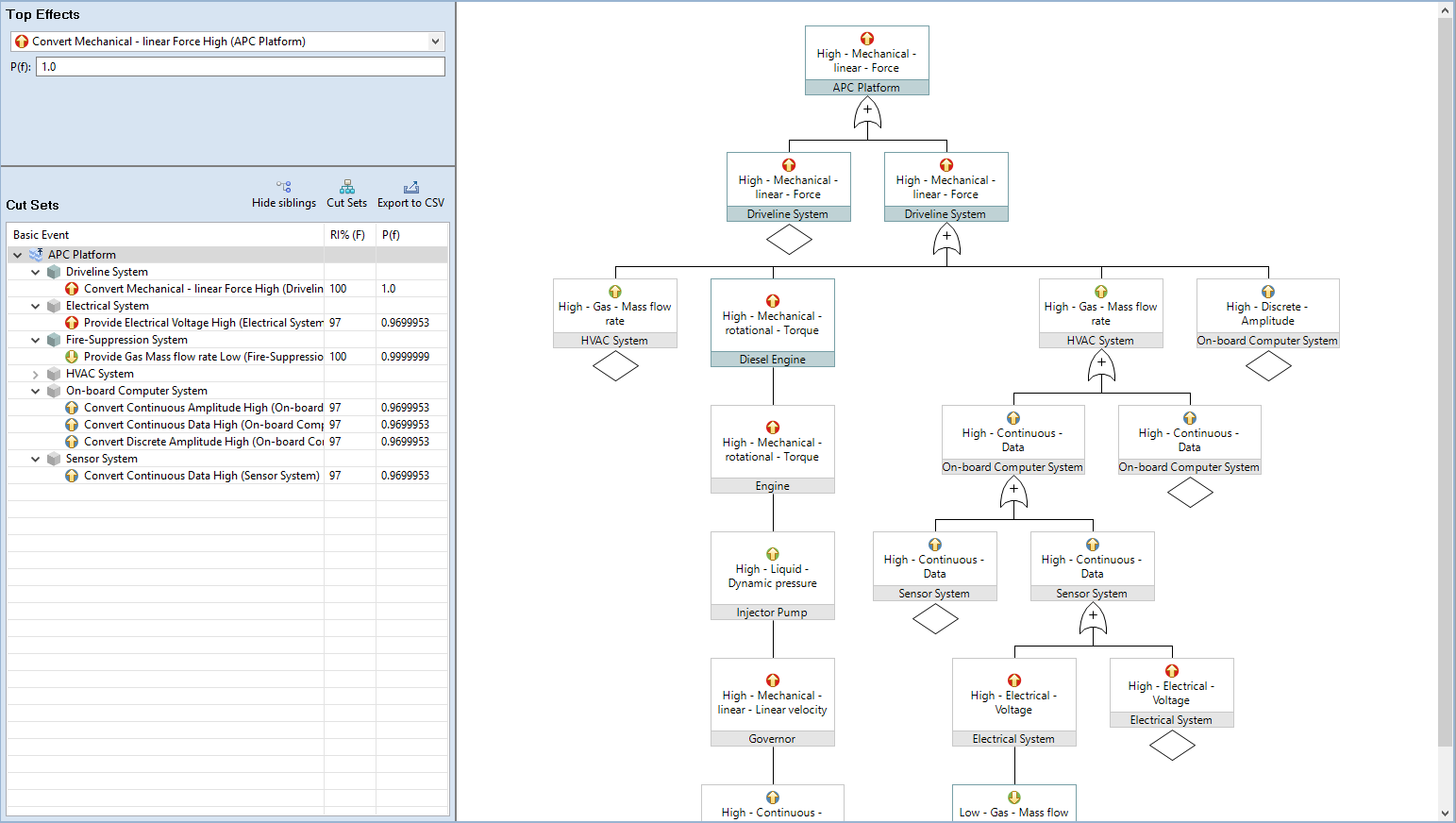
Fault Tree Analysis
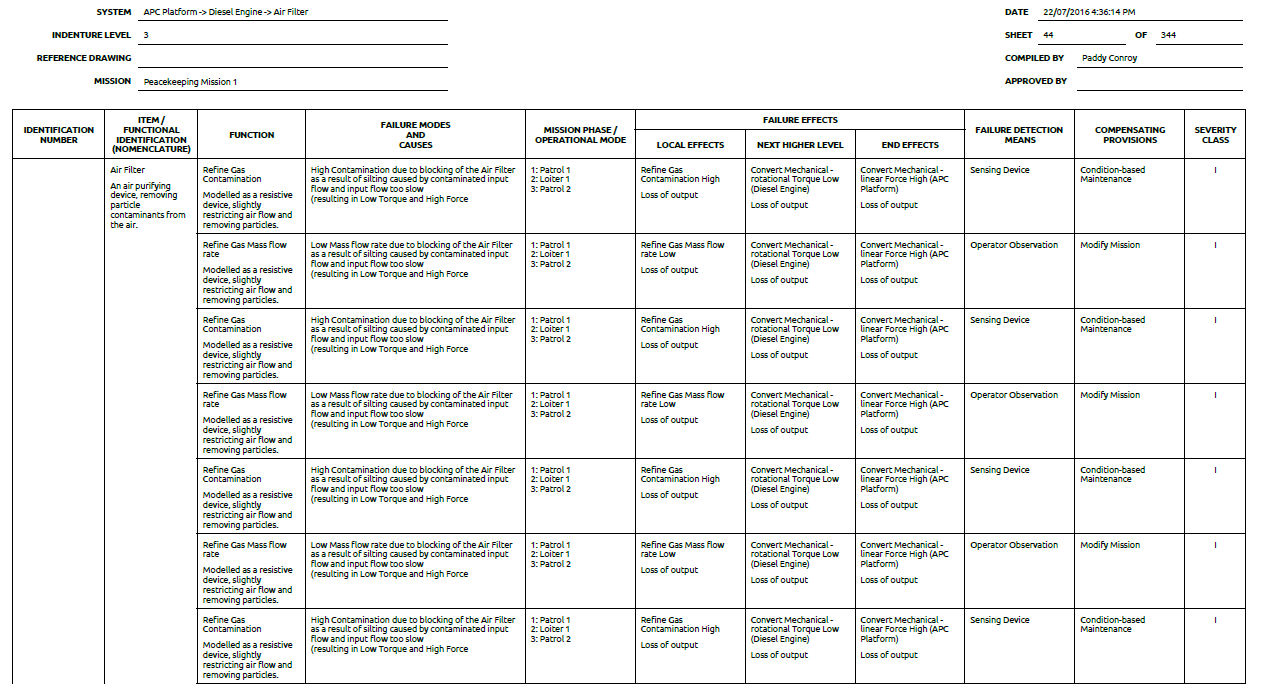
Failure Mode Effects Analysis
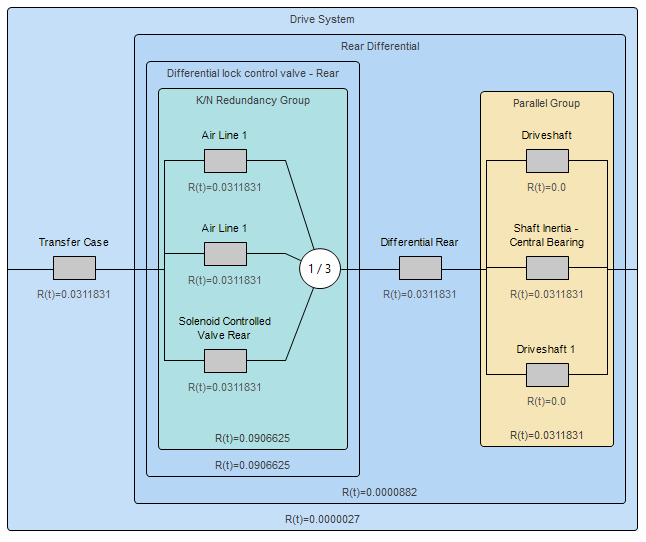
Reliability Bock Diagram
Reliability Centred Maintenance
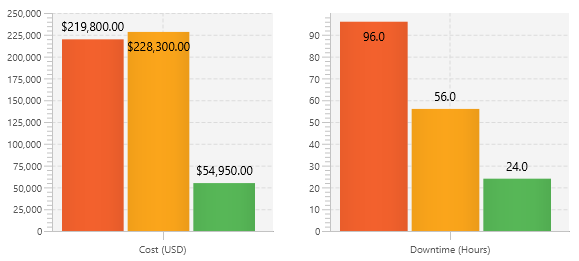
Reliability Allocation
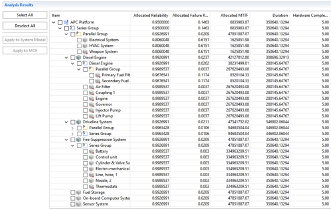
Mission Effectiveness Function List
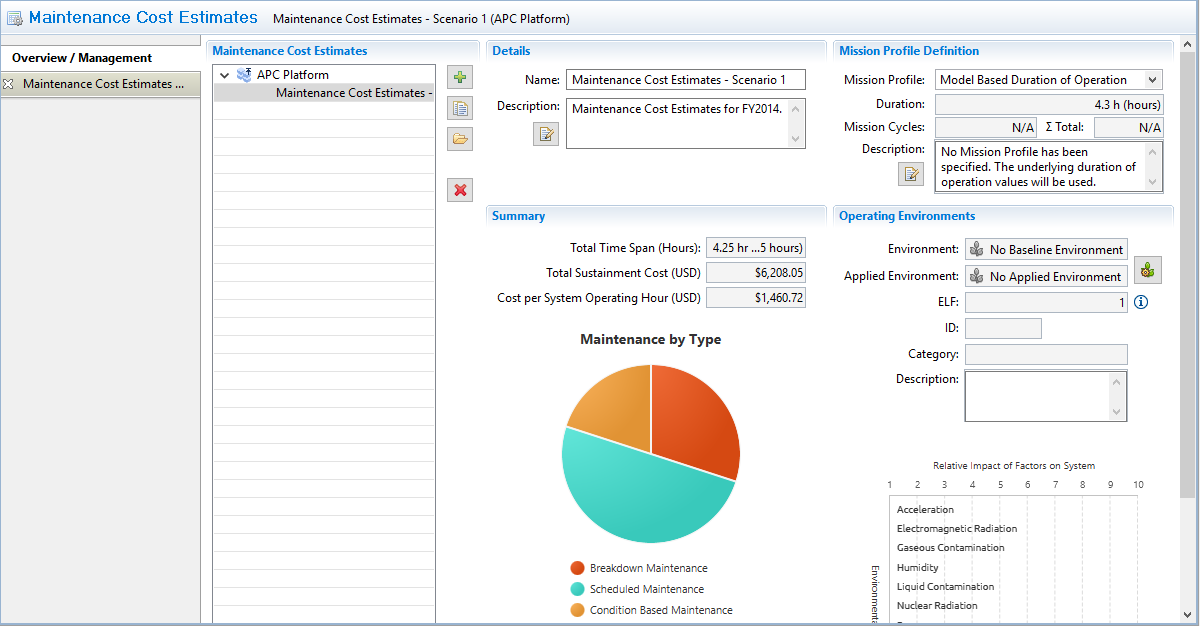
Maintenance Cost Estimate
PHM Design
Digital Risk Twin White-paper
A Digital Risk Twin revolutionizes how engineering teams can approach system safety, risk and reliability management and system maintainability. By integrating advanced analysis, automation, and visualization, a DRT addresses key challenges in RAMS engineering, enhancing both the efficiency and effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies and shifting the process left, while also closing the design loop. MADE and it's Digital Risk Twin technology not only improves current processes but also sets a foundation for future innovations in system safety, reliability and maintainability.
PHM Technology published a paper title 'The Digital Risk Twin - Enabling Model-based RAMS'. In this paper the Digital Risk Twin technology that enables organizations to realize the benefits of digital transformation for the RAMS domain is outlined.
The paper goes on to discuss the terminology for Digital Risk Twin (DRT) which better encapsulates the needs and driving risk/safety factors than a standard ‘design digital twin’ for RAMS companies/projects. The identified key attributes, deliverables raised in the system safety/risk assessment paragraph provides a RAMS-specific context for the DRT aligned with standard Digital Twin literature in the earlier sections.
The key findings of this paper are that a DRT, like all Digital Twins, must have a core set of fundamental aspects that are demonstrated to operate efficiently, as to be able to provide value and end benefits to the engineering community.
Related White-papers
 |
The Digital Risk Twin – Enabling Model-based RAMS While the definition of a Digital Twin (DT) is provided within recent literature, each DT should be designed to meet the specific requirements of the user. As RAMS is focused on the identification, understanding and mitigation of technical risk in a system, a RAMS engineer requires a DT that can autonomously establish the potential potential dependencies and impacts of functional and physical failures on a system, and auto-generate various analyses to identify the appropriate mitigation approach....... |

